TOP PAGE > Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
 Myanmar
Myanmar
General Information
 Formal Name: Republic of the Union of Myanmar
Formal Name: Republic of the Union of MyanmarLocated in the west of Indochina Island, Myanmar borders Thailand, Lao, PDR, Bangladesh and India. Land area is about 680,000 square kilometers. It faces the bay of Bengali and the Indian Ocean. Indo-Australia Plate and Eurasia Plate cause earthquake.
The capital is Naypyitaw. It has 51.92 million(2014 census) population. 70 percent of the population is Burma, while others are various national races.
Overview of Disasters
Fire, floods, cyclone are the frequent disasters.
Recent Major Disasters
Flood and Landslide (2019)
On August 2019, Myanmar faced floods in several parts of the country due to the heavy rains. As a consequence of heavy rain, landslide was affected the 82 dead and 49 injured. Approximately a total of 0.2 million people were affected while 201,133 people from 43,759 households were evacuated to 400 evacuation sites in affected areas. Mon State was the most seriously affected by this flood. (NDMC Situation Report)
Nationwide Floods (July and August 2015)
After the Cyclone Nargis 2008, the 2015 Nationwide floods were the worst for the country that ever record. The President of Myanmar had to declare Chin and Rakhine states, and Magway and Sagaing regions as announced disaster regions. The floods affected over 9 million people across 12 of Myanmar’s 14 states and regions. According to Department of Disaster Management (DDM) figures, 149 people died and the floods temporarily displaced over 1.6 million people from 405,958 households. Over 15,000 homes were destroyed as well as more than 840,000 acres of agricultural crops. The high winds and heavy rain also disrupted transportation, electricity and communications and flooded several townships. (ReliefWeb)
Cyclone Nargis (May 2008)
Cyclone Nargis hit Myanmar in May 2008 which killed 84,537, with the missing 53,836, injured 19,359. 450,000 houses were destroyed, with other 350,000 damaged. Total affected people were 2.4 million. Total economic loss was US$ 4.1 billion (Post-Nargis Joint Assessment- PONJA).
Disaster Management System
Legal System
The Disaster Management Law was enacted in 2013 and the Disaster Management Rules was prescribed in 2015. The Law was developed to be in line with Hyogo Framework for Action (2005-2015) and to comply with the ASEAN Agreement on Disaster Management and Emergency Response (AADMER). The Law focuses on risk information, preparedness, awareness and early warning, and data management for early warning systems.
Organization
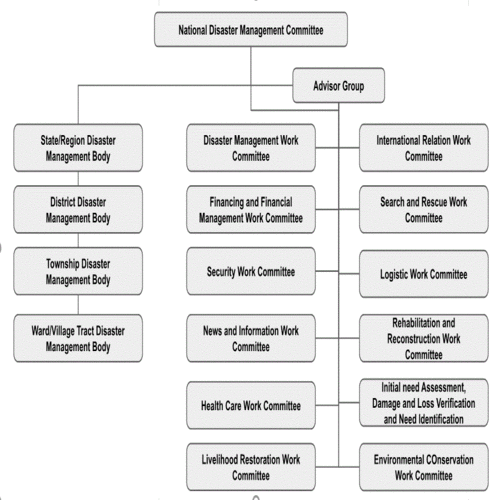 The Disaster Management Law (2013) provides for the establishment of the National Disaster Management Committee (NDMC) chaired by the Vice-President 2. The Committee is the supreme agency on disaster risk management (policy level, decision making, formulating strategies and overall supervision). The twelve work committees related to the specific areas of DRM and an advisory committee have been set up under NDMC (See the chart on the right). State/region, district, township and village tract-level DM bodies had also been formed respectively.
The Disaster Management Law (2013) provides for the establishment of the National Disaster Management Committee (NDMC) chaired by the Vice-President 2. The Committee is the supreme agency on disaster risk management (policy level, decision making, formulating strategies and overall supervision). The twelve work committees related to the specific areas of DRM and an advisory committee have been set up under NDMC (See the chart on the right). State/region, district, township and village tract-level DM bodies had also been formed respectively. Plan
The Myanmar Action Plan on Disaster Risk Reduction (MAPDRR) 2017 is a comprehensive and unified action plan for DRR with prioritized interventions across Myanmar till 2020. The vision of MAPDRR is to protect lives, economy, heritage and environment through an inclusive approach towards sustainable development in Myanmar. With a long-term vision and considering deep-rooted underlying drivers of disaster risk, it has been set an overall target for 2030. It aims to provide a base for mobilizing and leveraging, primarily, national and external resources and will provide a basis for result printed outcomes.
ADRC Counterpart
Country Report
Country Report 2022 (English Version, PDF file)Country Report 2021 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2020 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2018 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2014 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2013 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2006 (Japanese Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2006 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2002 (English Version, PDF file)

