TOP PAGE > Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
 China
China
General Information
 Formal Name: People’s Republic of China
Formal Name: People’s Republic of ChinaChina is located in eastern Eurasia. Having an area of approx. 9.6 million square kilometres, China enjoys the third largest land area in the world after Russia and Canada. Adjacent countries are: North Korea (east), Mongolia (north), Russia (northeast), Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan (northwest), India, Nepal and Bhutan (west and southwest), and Myanmar, Laos, Vietnam (south).
China boasts diverse landscapes and climates due to its size and geographical location. Landscapes are such as: high mountain ranges, fertile plains, vast deserts, plateaus, major rivers, extensive coastlines, and high-altitude region of Tibet with extreme climates. Diverse climate reflects such as tropical in south and sub-arctic in north.
The Capital is Beijing and China boasts with the largest population in the world of approx. 1.4 billion. China is home to a multi-ethnic population with roughly 90% of the population being Han Chinese making it the largest ethnic group and making up the majority of the population.
Overview of Disasters
Being a vast and geographically diverse country, China faces a range of disasters that can profoundly affect its people, infrastructure, and economy. These include: earthquakes, floods, typhoons, landslides, droughts, desertification, avalanches, hailstorms, wildfires, tornadoes, and occasional tsunamis. Among them, China experiences the significant impacts of monsoon weather and recurrent meteorological disasters, as well as regional and localized droughts, earthquakes, collapses, landslides, and debris flows in the hilly and mountainous areas and forest and grassland fires.
Recent Major Disasters
Torrential Rain (July 2020)
The torrential rain in southwest Chongqing Municipality left 11 dead and forced 21,500 residents to evacuate, according to local authorities. Some 550,000 residents in 31 districts or counties have been affected from the rainstorms. In addition, some 23,000 hectares of crops were damaged and over 1,000 houses were destroyed, said the statement. Continued days of torrential rains raised the water levels of the Yangtze and Wujiang rivers. Based on statements from the flood control and drought relief headquarters of the city, the water level at a hydrological station along Wujiang, a major tributary of the Yangtze River, rose by 5.55 meters to a staggering 225.03 meters.
Typhoon Nepartak (July 2016)
With heavy rains triggering floods, Typhoon Nepartak, affected 243 million people across 20 provinces. As of 28 July 2016, 417 flood-related deaths had been recorded, with 162 people still missing. It also led to at least the collapse of 41,000 houses. In addition, the rain has destroyed 295,200 hectares of crops. Floods and landslides also affected telecommunication and electricity facilities, halting or delaying traffic in some regions.
Sichuan Earthquake (May 2008)
A major earthquake occurred on 12 May 2008 in Sichuan province, claiming the lives of 69,227 people (in addition to 17,923 individuals reported as missing). This catastrophic event also led to direct economic losses reaching a staggering 1,053 billion yuan (equivalent to US$159 billion in 2018 values).
Disaster Management System
Legal System
More than 30 laws and regulations have been promulgated and implemented on disaster reduction, which include the Law on Water and Soil Conservation, the Law on Earthquake Prevention and Disaster Reduction, the Law on Fire-Fighting, the Meteorological Law and the Law on Production Safety.
Organization
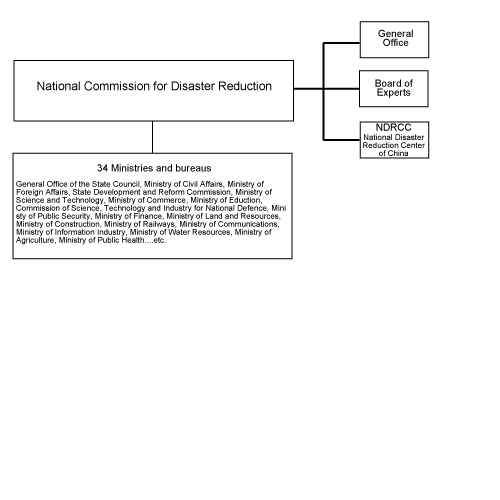 China National Commission for the International Decade on Natural Disaster Reduction was established in 1989. In 2000, it was renamed China Commission for International Disaster Reduction. In January of 2005, it was renamed as China National Committee for Disaster Reduction (NCDR), headed by a Vice Premier of the State Council. It is composed of 34 ministries and departments, including relevant military agencies and social groups. It functions as an inter-agency coordination body under the State Council, which is responsible for studying and formulating principles, policies and plans for disaster reduction, coordinating major disaster activities, giving guidance to local governments in their disaster reduction work, and promoting international exchanges and cooperation.
China National Commission for the International Decade on Natural Disaster Reduction was established in 1989. In 2000, it was renamed China Commission for International Disaster Reduction. In January of 2005, it was renamed as China National Committee for Disaster Reduction (NCDR), headed by a Vice Premier of the State Council. It is composed of 34 ministries and departments, including relevant military agencies and social groups. It functions as an inter-agency coordination body under the State Council, which is responsible for studying and formulating principles, policies and plans for disaster reduction, coordinating major disaster activities, giving guidance to local governments in their disaster reduction work, and promoting international exchanges and cooperation. Plan
In April 1998, the Chinese Government promulgated the National Natural Disaster Reduction Plan of the People’s Republic of China (1998 -2010), the first national disaster reduction plan formulated in accordance with the Ninth Five-Year National Economic and Social Development Plan and the 2010 Long-term Objective. The Disaster Reduction Plan identified includes: disaster reduction should be deeply considered in national economic and social development; prevention should be taken as the priority in combination with resistance and relief; The role of science, technology, and education should be incorporated in disaster reduction; the central and local governments as well as all social sectors should be to reduce disasters; and international exchange and cooperation should be strengthened.
ADRC Counterpart
Country Report
Country Report 2012 (English Version, PDF file)Country Report 2006 (Japanese Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2006 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1999 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1999 (Japanese Version, PDF file)

