TOP PAGE > Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
 Korea (the Republic of)
Korea (the Republic of)
General Information
 Formal Name: Republic of Korea
Formal Name: Republic of KoreaThe Republic of Korea (South Korea) is located in the southern part of the Korean Peninsula, covering a total area of 99,274 square kilometers. Approximately 70 percent of the land is mountainous, with plains mainly concentrated in the western and southern regions. The country has a temperate climate with four distinct seasons: hot and rainy summers, cold and dry winters, and mild spring and autumn periods.
With a population of about 52 million, South Korea is a democratic republic governed by a presidential system. Seoul is the capital and largest city, serving as the cultural, political, and economic center of the nation.
Overview of Disasters
Typhoon sometimes triggers torrential rains and subsequent floods. Heavy snowfall, landslides, storms, drought, heatwaves are the major disasters.
Recent Major Disasters
Heavy Rain (July 2023)
The heavy rain in July 2023 caused widespread damage across South Korea, leading to 50 fatalities and numerous landslides. Over 10,000 people were evacuated, and significant infrastructure was destroyed, including the Osong underground roadway in Cheongju, where a tragic flooding incident claimed multiple lives. The disaster highlighted the increasing impact of extreme weather events.
Heatwave (Summer 2022)
During the summer of 2022, an extreme heatwave hit South Korea, resulting in 34 deaths nationwide. The toll from the heatwave exceeded the fatalities caused by floods the same year, highlighting the increasing risks associated with extreme weather events.
These disasters underscore the growing impact of climate change and the need for proactive measures to mitigate and adapt to extreme weather conditions.
Floods and Landslides (August 2020)
In August 2020, record-breaking rainfall during the monsoon season caused widespread flooding and landslides across South Korea. The prolonged heavy rain, lasting 42 consecutive days, led to 14 fatalities and displaced over 1,000 residents
Disaster Management System
Legal System
The Act on Disaster Risk Management and Reduction enacted in 2008 stipulates the basics of the disaster management policies of Korea. There are other DM related laws including the Disaster and Safety Management Basic Act enacted in 2004, the Natural Disaster Countermeasures Act enacted in 1995, the Water and Wind related Disaster Insurance Act, the Act on Disaster Risk Management and Reduction of Reservoir and Dam enacted in 2008, the Special Law on Reduction of Disaster Risk and Emigration Measure in 2007.
Organization
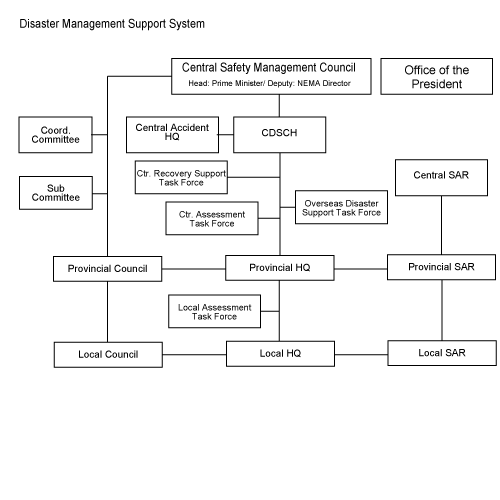 Prevention Phase
Prevention PhaseMinistry of the Interior and Safety (MOIS): Develops disaster prevention policies and manages disaster-prone areas.
Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport (MOLIT): Implements seismic standards and integrates disaster prevention into urban planning.BR> Ministry of Environment: Manages flood and landslide risks, focusing on climate change.
Local Governments: Conduct inspections and enforce safety regulations.
Preparedness Phase
National Fire Agency: Trains personnel for firefighting and rescue, conducts emergency simulations.
Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA): Issues early warnings for weather events and monitors seismic activity.
Flood Control Office & Korea Forest Service: Provide flood warnings, landslide alerts, and mitigation measures.
Local Governments and NGOs: Manage shelters, create response plans, and run public education programs.
Response Phase
Central Disaster and Safety Countermeasures Headquarters (CDSCH): Coordinates national disaster response efforts.
National Fire Agency & Police: Handle rescue, firefighting, and evacuation.
Ministry of National Defense: Provides military support for rescue and recovery.
Public Utilities: Restore essential services like electricity and water.
Recovery Phase
MOIS & Local Governments: Develop recovery plans, assess damage, and provide financial aid.
MOLIT: Rebuilds critical infrastructure with disaster-resistant measures.
Ministry of Environment: Restores ecosystems and manages environmental risks.
Red Cross & NGOs: Distribute relief supplies and provide psychological support.
Plan
South Korea’s disaster management framework operates at both national and municipal levels. At the national level, the National Basic Plan for Safety Management (NBPSM) provides a comprehensive strategy to address disaster risks through prevention, preparedness, response, and recovery, involving all stakeholders. At the municipal level, the Comprehensive Plan for Natural Disaster Reduction (CPNDR) focuses on localized risk assessments and tailored measures for natural hazards like floods, landslides, and droughts. Both plans integrate advanced technologies, public participation, and long-term planning to enhance disaster resilience. This dual-level approach ensures coordinated and region-specific disaster management across the country.
ADRC Counterpart
Country Report
Country Report 2024 (English Version, PDF file)Country Report 2008 (Japanese Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2006 (Japanese Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2006 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2002 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2001 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1999 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1999 (Japanese Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1998 (English Version, PDF file)

