TOP PAGE > Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
 Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea
General Information
 Formal Name: Independent State of Papua New Guinea
Formal Name: Independent State of Papua New GuineaPapua New Guinea is located in the south Pacific, occupying the eastern half of the island of New Guinea, New Britain and numerous offshore islands. It is surrounded by Australia, Solomon Islands, Indonesia and Micronesia. Land area is 462,000 square kilometers. The Bismarck Range and the Owen Stanley Range cut across the New Guinea Island. Tropical Climate, northwest monsoon (December to March), southeast monsoon (May to October); slight seasonal temperature variation.
The capital is Port Moresby. Population, 6,187,000, consists of the Melanesian.
Overview of Disasters
Earthquakes, river flooding, landslides, dam break, coastal erosion and tsunami are the major disasters in Papua New Guinea.
Recent Major Disasters
Aitape Tsunami (July 1998)
On 17 July 1998, there was a strong earthquake of 7.1 in the Richter scale off the northwest coast of Papua New Guinea. The earthquake triggered three big waves of tsunami whose maximum height was 15m. More than 2,200 people died, about 700 people seriously injured, 10,000 people were forced to relocate.
Cyclone Guba (November 2007)
Tropical Cyclone Guba struck Papua New Guinea on 12-16 November 2007, bringing torrential rains and high tides which have claimed more than 70 lives and affected 145,000 people.
Volcanic Eruption (September 1994)
Two volcanic cones of the Rabaul volcano in the eastern New Britain Island began to erupt on 19 September 1994. Strong explosions have spread fumes and ash over surrounding areas including the capital of Rabaul. Thanks to the early warning activities of the volcanic research center, 100,000 people evacuated, although 5 people were victimized.
Disaster Management System
Legal System
Disaster Management Act was promulgated in 1987. A new law is under drafting in order to adjust to the contemporary disaster management measures and administrative reforms in the local government levels.
The Public Health Act, RPNG Constabulary Act, Internal Revenue Act and Insurance Act also contain stipulations on disaster management.
Papua New Guinea also has the Disaster Management Tools which identify its DM policy and guidelines.
The Public Health Act, RPNG Constabulary Act, Internal Revenue Act and Insurance Act also contain stipulations on disaster management.
Papua New Guinea also has the Disaster Management Tools which identify its DM policy and guidelines.
Organization
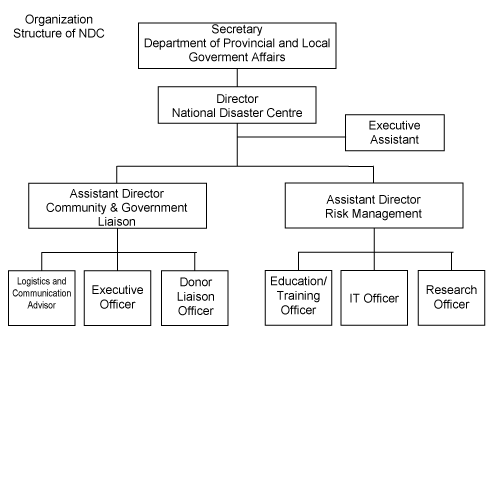 The National Disaster Centre (NDC) is established by an Act of Parliament, the Disaster Management Act Chapter 403 of 1987.
The National Disaster Centre (NDC) is established by an Act of Parliament, the Disaster Management Act Chapter 403 of 1987.It is part of the Department of Provincial & Local Government Affairs, and exists under legislation to provide the necessary and appropriate disaster management services to the government and the people of Papua New Guinea. It is responsible for managing natural and human-caused disasters in Papua New Guinea. The office is headed by Director, who is appointed by the National Executive Council (NEC).
Plan
The current Disaster Management Plan (1987) was reviewed in 1999, but suggested changes were not pursued. The National Disaster Centre has conducted an internal review and has drafted a new Disaster Management Plan that reflects changes in contemporary disaster management thinking and practices, as well as changes to PNG government policies, particularly the Organic Laws on the Provincial and Local Level Governments. The NDC is currently drafting the National Response Action Plan (NRAP).

