TOP PAGE > Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
 Singapore
Singapore
General Information
 Formal Name: Republic of Singapore
Formal Name: Republic of SingaporeSingapore is located in the latitude 1.17 degrees and the longitude 103.51 degrees. It borders Malaysia at the Johore Straits. Singapore consists of the Singapore Island and the surrounding small islands. Plain spreads in the Singapore Island. Land area is 699 square kilometers. Located on the equator, the weather is hot and humid throughout the year. Unclear distinction between dry and rainy season. It is affected by the northeast monsoon (December to early March) the southwest monsoon (June to September). In December and April, it has high precipitation. 75 percent of the 4.59 million population is Chinese, 14 percent Malay, 9 percent Indians.
Overview of Disasters
Though Singapore is spared from natural disasters such as earthquakes, typhoons and volcanic eruptions, the challenges for the emergency services are in preventing and mitigating man-made disasters in a highly urbanised environment with many high-rise buildings and Hazardous Material (HazMat) industries.
Recent Major Disasters
Haze (June 2013-)
Singapore has been affected by severe smoke haze due to open buring and forest fires having been taken place in Sumatra Island of Indonesia periodically. It can be made worse by dry seasons.
Disaster Management System
Legal System
The Civil Defence Act (1986) provides the legal framework for, amongst other things, the declaration of a state of emergency and the mobilisation and deployment of operationally ready national service rescuers. The Fire Safety Act, and the Civil Defence Shelter Act are among the relevant acts on emergency management.
Organization
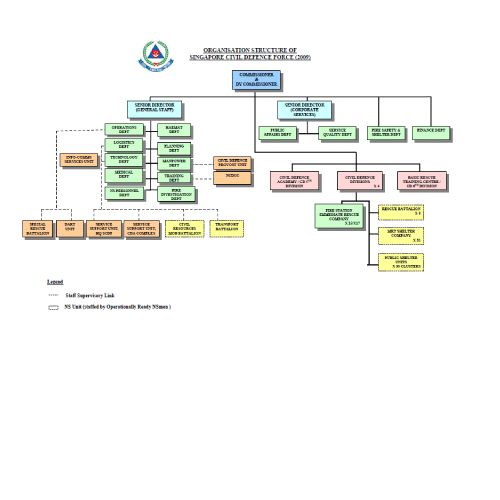 The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is the principal policy-making government body for safety and security in Singapore. In the event of a national disaster, MHA leads at the strategic level of incident management. At the tactical level, Singapore Civil Defence Force (SCDF) will coordinate the planning and execution of the multi agency response to mitigate the impact of the disaster. SCDF provides effective 24-hour fire fighting, rescue and emergency ambulance services. Other functions include educating the community as well as mobilizing the community to be more involved in safety and security. SCDF also enforces fire safety requirements and oversees the civil defence shelter construction programme and the public warning system.
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is the principal policy-making government body for safety and security in Singapore. In the event of a national disaster, MHA leads at the strategic level of incident management. At the tactical level, Singapore Civil Defence Force (SCDF) will coordinate the planning and execution of the multi agency response to mitigate the impact of the disaster. SCDF provides effective 24-hour fire fighting, rescue and emergency ambulance services. Other functions include educating the community as well as mobilizing the community to be more involved in safety and security. SCDF also enforces fire safety requirements and oversees the civil defence shelter construction programme and the public warning system. Plan
SCDF has developed the Operations Civil Emergency (Ops CE) Plan, a national response plan for civil emergencies which outlines the work of SCDF and all the Related Agencies (RAs)4 in the management of a major disaster. Under this plan, SCDF is overall-in-charge of the multi-agency response.
ADRC Counterpart
Country Report
Country Report 2006 (Japanese Version, PDF file)Country Report 2006 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2003 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2002 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2001 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1999 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1999 (Japanese Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1998 (English Version, PDF file)

