TOP PAGE > Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
 Cambodia
Cambodia
General Information
 Formal Name: Kingdom of Cambodia
Formal Name: Kingdom of CambodiaGeographical Location: Cambodia is located in Southeast Asia, bordered by Vietnam to the east, Thailand to the west, and Lao PDR to the north. To the south, it is bounded by the Gulf of Thailand.
Land Area: Covering approximately 181,035 square kilometers, Cambodia boasts diverse geography, including the Mekong River, which traverses 500 kilometers of its territory, and the iconic Tonle Sap Lake in the mid-western region. Population: According to the latest data from WorldOmeter, Cambodia is home to nearly 17 million people, making it one of the most populous countries in Southeast Asia. The population is predominantly composed of Khmer (90%) and various ethnic minorities, including Cham, Chinese, Vietnamese, and indigenous mountainous tribes.
Administrative Divisions: The nation is divided into 24 provinces, with its capital city being Phnom Penh, serving as the political, socio-economic, and cultural hub.
Climate: Cambodia experiences a tropical climate dominated by the monsoon. Notably, the monsoon season, which typically occurs from May to October, plays a pivotal role in its climate patterns. During the monsoon season, Cambodia receives a substantial portion of its annual rainfall, accounting for almost 75% of its total precipitation. The dry season, spanning from November to April, offers a respite from heavy rainfall, creating favorable conditions for various outdoor activities and agricultural activities.
Overview of Disasters
Susceptibility of Cambodia to natural disasters, including floods, droughts, and storms, can be attributed to its unique historical context as a nation recovering from a period of civil conflict. Furthermore, with a predominantly agrarian economy, it presents challenges and vulnerabilities regarding natural disasters.
Cambodia faces challenges related to its capacity, infrastructure, and institutional constraints, which, when compounded, heighten its vulnerability to climate variability and change. In this context, it is important to note that storms also pose a significant threat to Cambodia, adding to the complexity of its disaster risk landscape. Over the past decade, Cambodia has grappled with recurrent natural disasters, including droughts, floods, and storms.
(Source: Climate Change Knowledge Portal, World Bank)
Cambodia faces challenges related to its capacity, infrastructure, and institutional constraints, which, when compounded, heighten its vulnerability to climate variability and change. In this context, it is important to note that storms also pose a significant threat to Cambodia, adding to the complexity of its disaster risk landscape. Over the past decade, Cambodia has grappled with recurrent natural disasters, including droughts, floods, and storms.
(Source: Climate Change Knowledge Portal, World Bank)
Recent Major Disasters
Floods (2022)
Severe flooding from May 2022 resulted in significant damage.
From September 1st to October 11th, approximately 85,482 households in 14 provinces were affected, leading to evacuations, casualties, and damage to houses, infrastructure, and agricultural land.
The risk of severe floods persisted until the end of October.
Flood (September-October 2011)
TOP PAGE > Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
CambodiaCambodia
General Information
CambodiaFormal Name: Kingdom of Cambodia
Geographical Location: Cambodia is located in Southeast Asia, bordered by Vietnam to the east, Thailand to the west, and Lao PDR to the north. To the south, it is bounded by the Gulf of Thailand.
Land Area: Covering approximately 181,035 square kilometers, Cambodia boasts diverse geography, including the Mekong River, which traverses 500 kilometers of its territory, and the iconic Tonle Sap Lake in the mid-western region. Population: According to the latest data from WorldOmeter, Cambodia is home to nearly 17 million people, making it one of the most populous countries in Southeast Asia. The population is predominantly composed of Khmer (90%) and various ethnic minorities, including Cham, Chinese, Vietnamese, and indigenous mountainous tribes.
Administrative Divisions: The nation is divided into 24 provinces, with its capital city being Phnom Penh, serving as the political, socio-economic, and cultural hub.
Climate: Cambodia experiences a tropical climate dominated by the monsoon. Notably, the monsoon season, which typically occurs from May to October, plays a pivotal role in its climate patterns. During the monsoon season, Cambodia receives a substantial portion of its annual rainfall, accounting for almost 75% of its total precipitation. The dry season, spanning from November to April, offers a respite from heavy rainfall, creating favorable conditions for various outdoor activities and agricultural activities.
Overview of Disasters
Susceptibility of Cambodia to natural disasters, including floods, droughts, and storms, can be attributed to its unique historical context as a nation recovering from a period of civil conflict. Furthermore, with a predominantly agrarian economy, it presents challenges and vulnerabilities regarding natural disasters.
Cambodia faces challenges related to its capacity, infrastructure, and institutional constraints, which, when compounded, heighten its vulnerability to climate variability and change. In this context, it is important to note that storms also pose a significant threat to Cambodia, adding to the complexity of its disaster risk landscape. Over the past decade, Cambodia has grappled with recurrent natural disasters, including droughts, floods, and storms.
(Source: Climate Change Knowledge Portal, World Bank)
Recent Major Disasters
Flood (September-October 2011)
In 2011, flood affected 350,000 households (over 1.5 million people) and 52,000 households were evacuated. 18 out of 24 provinces in Cambodia were affected; 4 provinces along Mekong River and Tonle Sap were worst hit; 250 people died and 23 people were injured as result of the flood. 431,000 hectares of transplanted rice fields were affected and 267,000 hectares of rice fields were damaged. 925 kilometers of the national, provincial and urban roads were affected and 360 kilometers of the roads were damaged. The floods in 2011 caused an estimated loss at 630 million USD.
Drought (2011-12)
In 2011, drought affected 3,804 hectares of rice fields. Furthermore, in 2012, drought affected 14,190 hectare of rice fields and completely destroyed crops of 3,151 hectares.
Disaster Management System
Legal System
Cambodia has enacted a comprehensive Law on Disaster Management in 2015, providing a robust legal framework for disaster preparedness, response, and recovery.
Law on Disaster Management (Source: IFRC, English version)
Law on Disaster Management (Source: IFRC, English version)
Organization
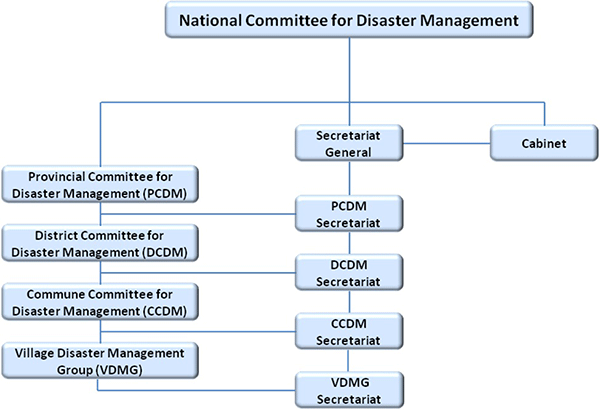 The National Committee for Disaster Management (NCDM), headed by the Prime Minister, serves as the central coordinating body.
The NCDM Secretariat leads and coordinates disaster management efforts at the national level.
Disaster management is decentralized through Provincial Committees for Disaster Management (PCDM), District Committees for Disaster Management (DCDM), and Commune Committees for Disaster Management (CCDM).
Village Disaster Management Groups (VDMG) operate at the grassroots level, actively participating in local disaster management activities.
The National Committee for Disaster Management (NCDM), headed by the Prime Minister, serves as the central coordinating body.
The NCDM Secretariat leads and coordinates disaster management efforts at the national level.
Disaster management is decentralized through Provincial Committees for Disaster Management (PCDM), District Committees for Disaster Management (DCDM), and Commune Committees for Disaster Management (CCDM).
Village Disaster Management Groups (VDMG) operate at the grassroots level, actively participating in local disaster management activities. Plan
Disaster management system of Cambodia underscores its commitment to enhancing disaster preparedness, response, and mitigation measures. Effective coordination among government agencies, humanitarian entities, and development partners is integral to its disaster prevention efforts. There are the following DRM related plans in Cambodia.
- National Strategy Development Plan (NSDP) 2009-2013
- Strategic National Action Plan for Disaster Risk Reduction (SNAP) 2008-2013
- National Action Plan for Disaster Risk Reduction 2014-2018 (drafted & adopted by 2014)
- National Comprehensive Avian and Human Influenza Plan (Multi-Sectoral Pandemic Preparedness and Response Plan)
- Community Based Disaster Risk Management Plan (CBDRM)
- National Contingency Plan for Flood and Drought (being revised)
- National Strategy Development Plan (NSDP) 2009-2013
- Strategic National Action Plan for Disaster Risk Reduction (SNAP) 2008-2013
- National Action Plan for Disaster Risk Reduction 2014-2018 (drafted & adopted by 2014)
- National Comprehensive Avian and Human Influenza Plan (Multi-Sectoral Pandemic Preparedness and Response Plan)
- Community Based Disaster Risk Management Plan (CBDRM)
- National Contingency Plan for Flood and Drought (being revised)
ADRC Counterpart
Country Report
Cambodia Disaster Loss and Damage Analysis Report (1996-2013) (English Version, PDF file)Country Report 2013 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2006 (Japanese Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2006 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2003 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2002 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1999 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1999 (Japanese Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1998 (English Version, PDF file)

