TOP PAGE > Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
General Information
 Formal name: People(apostrophe)s Republic of Bangladesh
Formal name: People(apostrophe)s Republic of BangladeshBangladesh is located in South Asia, bordered by between India and Myanmar, and faces the Bay of Bengal. Land area is 147,570 square kilometers. Bangladesh is a low-lying deltaic country in South Asia formed by the Ganges, the Brahmaputra and the Meghna rivers. More than 310 rivers and tributaries have made this country a land of rivers. Most of the country is covered with flat alluvial plain, yet there are hills in the southeast part. The country has the world’s longest unbroken sandy beach of 120km, sloping gently down to the blue waters of the Bay of Bengal. Bangladesh has a tropical monsoon climate characterized by wide seasonal variations in rainfall, high temperatures, and high humidity. Three seasons are generally recognized: a hot, muggy summer from March to June; a hot, humid and rainy monsoon season from June to November; and a warm-hot, dry winter from December to February.
The capital is Dhaka. Out of 157,220,520 people, 98 percent are the Bengali, among them 90.4% Muslim, 8.2 percent Hindu, 0.7 percent Buddhist and 0.6 percent Christians.
Overview of Disasters
Bangladesh has a long history of natural disasters. Between 1980 and 2008, it experienced 219 natural disasters. The geographical location, land characteristics, multiplicity of rivers and the monsoon climate render Bangladesh highly vulnerable to natural hazards. The coastal morphology of Bangladesh influences the impact of natural hazards on the area. Bangladesh suffers from floods, cyclones, storm surge, river bank erosion, earthquake, drought, salinity intrusion, fire and tsunami. Cyclones and floods particularly caused massive damages. Cyclones occurred in 1970, 1991, 2007 and 2009 and killed 364,000, 136,000, 3,363 and 190 respectively.
Recent Major Disasters
Cyclone Aila (May 2009)
Cyclone Aila hit the Bangladesh on Monday 25 May 2009 and has produced substantial damage across areas of southern Bangladesh. It caused 190 people dead and 3,935,341 people affected. The total damage was USD270 million.
Cyclone Sidr (November 2007)
Cyclone Sidr hit the coastal areas on 15 November 2007. It affected 8,978,541 people and killed 4,234. The economic damage caused by the cyclone is USD2.3 billion.
Cyclone (April 1991)
A cyclone occurred in April 1991 in Chittagong killed 138,866 people and affected 15,438849 people. The total damage was UD$1.78 billion.
Disaster Management System
Legal System
Disaster Management Act (2012)was adopted after collective efforts given by the GoB and development and civil society actors to create a legislative tool under which disaster and emergency management will be undertaken. The objectives of the Act are substantial reduction of the overall risks of disasters to an acceptable level with appropriate risk reduction interventions, effective implementation of post disaster emergency response, rehabilitation and recovery measures, provision of emergency humanitarian assistance to the most vulnerable community people, strengthening of institutional capacity for effective coordination of disaster management involving government and non-government organizations and establishing a disaster management system capable of dealing with all hazards for the country.
The National Disaster Management Policy, 2015, is formulated to define the national perspective on disaster risk reduction and emergency management, and to describe the strategic framework, and national principles of disaster management in Bangladesh.
Standing Orders on Disaster (SOD, 2019) provides a detailed institutional framework for disaster risk reduction and emergency management.
In addition to these legislative frameworks on disaster management there are some sectoral polices which indirectly support disaster risk management activities in different ways in Bangladesh. These are National Debris Management Guideline 2015, Policy Guideline of Management of Dead after Disasters 2016, Bangladesh Climate Change Strategy and Action Plan, National Food and Agriculture Policy, National Education Policy, National Child Policy and Children Act, National Women Advancement Policy, National Water Policy 1999.
The National Disaster Management Policy, 2015, is formulated to define the national perspective on disaster risk reduction and emergency management, and to describe the strategic framework, and national principles of disaster management in Bangladesh.
Standing Orders on Disaster (SOD, 2019) provides a detailed institutional framework for disaster risk reduction and emergency management.
In addition to these legislative frameworks on disaster management there are some sectoral polices which indirectly support disaster risk management activities in different ways in Bangladesh. These are National Debris Management Guideline 2015, Policy Guideline of Management of Dead after Disasters 2016, Bangladesh Climate Change Strategy and Action Plan, National Food and Agriculture Policy, National Education Policy, National Child Policy and Children Act, National Women Advancement Policy, National Water Policy 1999.
Organization
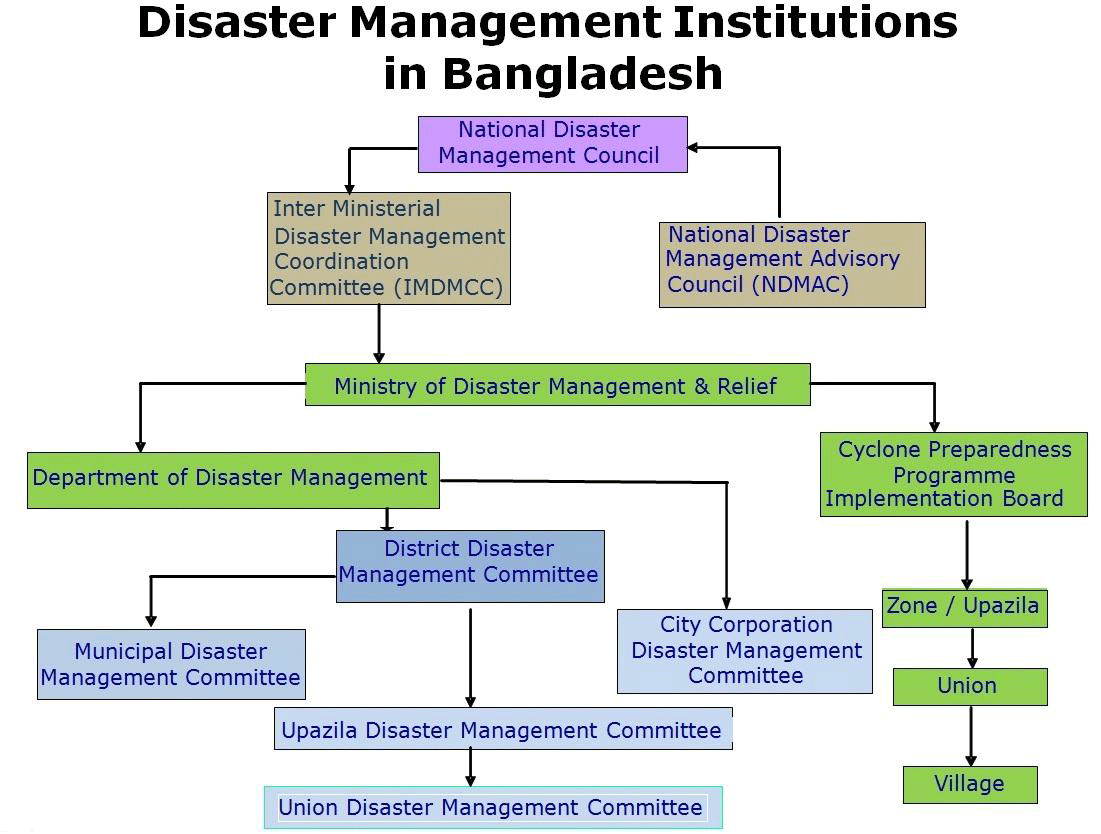 A series of inter-related institutions, at both national and sub-national levels have been created for disaster management. As per the Rules of Business of the Government of Bangladesh, the Ministry of Disaster Management and Relief (MoDMR) is mandated to formulate policies, prepare plans, and monitor and coordinate all aspects of disaster activities. The field level activities of MoDMR are carried out by two subordinate offices e.g. the Department of Disaster Management (DDM) and Cyclone Preparedness Programme (CPP), While DDM is responsible for dissemination of all information on natural disasters, including flood information at community level, flood preparedness, awareness raising and capacity building activities, and also is responsible for conducting relief and rehabilitating operations with the help of district and upazila administrations.
A series of inter-related institutions, at both national and sub-national levels have been created for disaster management. As per the Rules of Business of the Government of Bangladesh, the Ministry of Disaster Management and Relief (MoDMR) is mandated to formulate policies, prepare plans, and monitor and coordinate all aspects of disaster activities. The field level activities of MoDMR are carried out by two subordinate offices e.g. the Department of Disaster Management (DDM) and Cyclone Preparedness Programme (CPP), While DDM is responsible for dissemination of all information on natural disasters, including flood information at community level, flood preparedness, awareness raising and capacity building activities, and also is responsible for conducting relief and rehabilitating operations with the help of district and upazila administrations.The Comprehensive Disaster Management Programme (CDMP) is established to support the disaster management activities of relevant organizations as well as MoDMR.
Plan
National Plan for Disaster Management (NPDM) 2021-25 is the revised version of NPDM 2015-2020 prepared by the Ministry of Disaster Management and Relief (MoDMR), based on wider consultations with the relevant ministries, departments, donors, academic institutions, NGOs, research organizations, private sector and development partners.
NPDM 2021-25 is based on the four key principles of disaster risk management, namely preparedness, early warning and alert, emergency response, and rehabilitation, reconstruction and recovery adopted from Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (SFDRR) and Standing Order on Disaster (SOD).
This plan provides context, legal background, implementation status of previous plans and likely situation of Bangladesh in the changing disaster risk context.
ADRC Counterpart
Country Report
Country Report 2021 (English Version, PDF file)Country Report 2020 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2013 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2011 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2010 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2006 (Japanese Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2006 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2003 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1999 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1999 (Japanese Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1998 (English Version, PDF file)
Disaster Information (The latest 10)
・2024/05/26 : Tropical Cyclone
・2023/05/11 : Tropical Cyclone
・2022/10/24 : Tropical Cyclone

