TOP PAGE > Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
 Türkiye
Türkiye
General Information
 Formal Name: Republic of Türkiye
Formal Name: Republic of TürkiyeTürkiye is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian peninsula in Western Asia, with a smaller portion on the Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe. Türkiye is bordered by Greece and Bulgaria to its northwest; Georgia to its northeast; Armenia, the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhichevan and Iran to the east; and Iraq and Syria to the south, covering the area of 785,347 square kilometers with a total coastline of 8,430 km. The population residing in Türkiye was 85,664,944 people as of 31 December 2024. Istanbul, where 18.3% of Türkiye’s population resides, is Türkiye’s largest city in terms of population with 15,701,602 people, while 5,864,049 people reside in Ankara, the Capital City.
Overview of Disasters
Due to its geological and topographic structure and climatic features, Türkiye frequently faces disasters. Besides loss of lives, disasters also bring about significant economic loss for Türkiye. Various disasters often occur in Türkiye at various times. Earthquakes, floods, landslides, avalanches and rock falls are among the most frequent disasters experienced in Türkiye.
Recent Major Disasters
Earthquake (6 February 2023)
According to the records of the AFAD, Earthquake Department (DDB), an earthquake with an instrumental magnitude of Mw: 7.7 occurred in Pazarcık (Kahramanmaraş) district at 04:17 local time. While the aftershocks of this earthquake continued, the second earthquake with an instrumental magnitude of Mw 7.6 occurred in Elbistan (Kahramanmaraş) district at 13:24 on the same day and the Defne (Hatay) earthquake with a magnitude of Mw 6.4 occurred on 20 February 2023. Total of 5,649,317 houses in the 11 provinces affected by the earthquakes, and 1,929,313 of these houses were damaged. Damage was detected in 68.1% of the houses in Adıyaman, 57.8% in Kahramanmaraş, 55.6% in Malatya and 50.8% in Hatay, which were among the provinces most damaged by the earthquake. The number of deaths in the earthquakes is 53,735 and the number of injuries is 107,213.
Flood (11 August 2021)
The Western Black Sea flood disaster affected the provinces of Kastamonu, Sinop and Bartın due to floods, inundations and landslides that occurred as a result of heavy rainfall in the Western Black Sea Section of Türkiye’s Black Sea Region on 11 August 2021. A total of 97 people lost their lives and 228 people were injured in the floods.
Earthquake (17 August 1999)
The 7.4 magnitude earthquake on 17 August 1999 that centered around Golcuk in the province of Kocaeli with a succession of several major earthquakes killed 20,000 persons and injured 50,000 persons.
Disaster Management System
Legal System
Because of the lessons learned from management and coordination problems in particular from the earthquake of 1999 and various subsequent disasters, the former post-disaster central-to-local crisis management mentality was replaced with pre-disaster mitigation activities and local-to-central risk management. In this framework, with the founding law passed in 2009, AFAD was established at the central level, with Disaster and Emergency Directorates attached to Governorates established at the local level. Türkiye Integrated Disaster Management System was established and Türkiye Disaster Response Plan, Türkiye Disaster Risk Reduction Plan and Provincial Risk Reduction Plans were prepared for this system.
Law No. 5902 on Organization and Functions of the Disaster and Emergency Management Authority (AFAD)
Organization
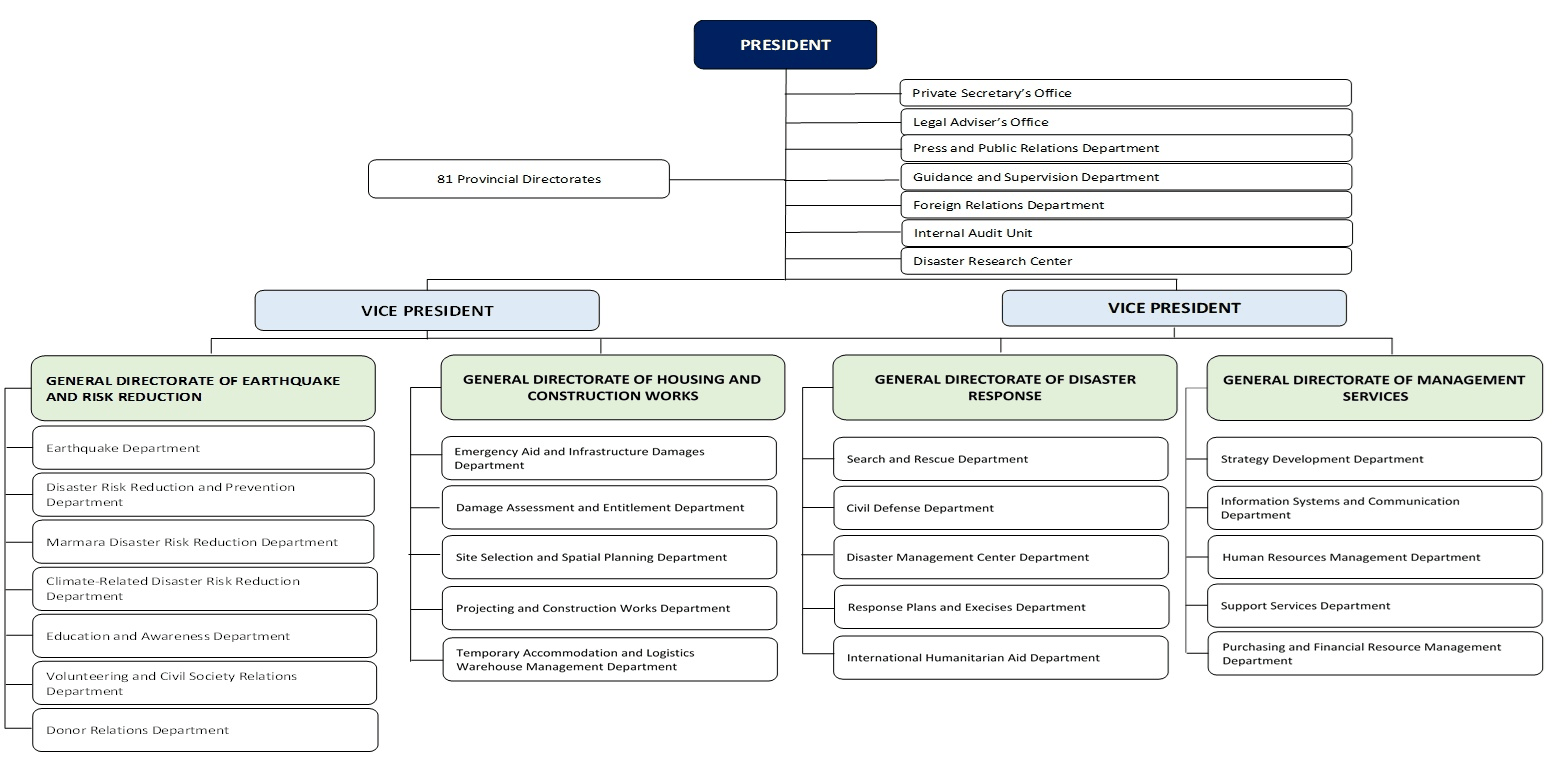 Disaster and Emergency Management Authority (AFAD) under the Ministry of Interior (previously under the office of Prime Ministry), an institution working to prevent disasters and minimize disaster-related damages, plan and coordinate post-disaster response, and promote cooperation among various government agencies.
Disaster and Emergency Management Authority (AFAD) under the Ministry of Interior (previously under the office of Prime Ministry), an institution working to prevent disasters and minimize disaster-related damages, plan and coordinate post-disaster response, and promote cooperation among various government agencies.In this regard, AFAD introduced a novel disaster management model which prioritizes Türkiye’s transition from crisis management to risk management – which came to be known as the Integrated Disaster Management System.
AFAD currently has 81 provincial branches across Turkey in addition to 11 search and rescue units.
Plan
AFAD Strategic Plan
Mission
To effectively manage disaster and emergency processes with a risk-focused disaster management approach, to ensure coordination with all relevant stakeholders and to produce policies in this area.
Vision
To create a society resilient to disasters
Objectives
Objective 1: To increase the effectiveness of disaster risk reduction efforts
Objective 2: To be best prepared for disasters and emergencies institutionally and socially
Objective 3: To ensure that disaster response processes are carried out quickly, effectively and in a coordinated manner
Objective 4: To ensure that disaster and emergency recovery processes are carried out quickly, effectively and in a coordinated manner
Objective 5: To become a global actor by increasing international effectiveness Objective 6: To be an institution that is strong and open to innovation in terms of knowledge, technological infrastructure and human resources
Türkiye Disaster Response Plan
Purpose
To define the roles and responsibilities of the working groups and coordination units that will take part in disaster and emergency response activities and to determine the basic principles of pre-disaster, during and post-disaster response planning.
Türkiye Disaster Risk Reduction Plan (TARAP)
Purpose
To prevent or minimize the physical, social, economic, environmental, psychological damages and losses that may be caused by disasters, to create durable, safe, prepared, sustainable, disaster-resistant living environments, and to determine the basic principles of disaster risk reduction activities that need to be prepared and implemented before a disaster.
TARAP includes ministries, institutions and organizations, private sector, NGOs and real persons who will carry out disaster risk reduction activities for all types and sizes of disasters that may occur in Türkiye.
Mission
To effectively manage disaster and emergency processes with a risk-focused disaster management approach, to ensure coordination with all relevant stakeholders and to produce policies in this area.
Vision
To create a society resilient to disasters
Objectives
Objective 1: To increase the effectiveness of disaster risk reduction efforts
Objective 2: To be best prepared for disasters and emergencies institutionally and socially
Objective 3: To ensure that disaster response processes are carried out quickly, effectively and in a coordinated manner
Objective 4: To ensure that disaster and emergency recovery processes are carried out quickly, effectively and in a coordinated manner
Objective 5: To become a global actor by increasing international effectiveness Objective 6: To be an institution that is strong and open to innovation in terms of knowledge, technological infrastructure and human resources
Türkiye Disaster Response Plan
Purpose
To define the roles and responsibilities of the working groups and coordination units that will take part in disaster and emergency response activities and to determine the basic principles of pre-disaster, during and post-disaster response planning.
Türkiye Disaster Risk Reduction Plan (TARAP)
Purpose
To prevent or minimize the physical, social, economic, environmental, psychological damages and losses that may be caused by disasters, to create durable, safe, prepared, sustainable, disaster-resistant living environments, and to determine the basic principles of disaster risk reduction activities that need to be prepared and implemented before a disaster.
TARAP includes ministries, institutions and organizations, private sector, NGOs and real persons who will carry out disaster risk reduction activities for all types and sizes of disasters that may occur in Türkiye.
ADRC Counterpart
Country Report
Country Report 2024 (English Version, PDF file)Country Report 2019 (English Version, PDF file)

